재난 응급의료에 대한 이야기
재난 응급의료! 워낙 크고 작은 재난들이 많이
이뤄지다보니, 20년전 대량재해 자료에서 변하지 않았던 재난의료에 대한 내용도 점차 발전된 것 같다.
---------------------------------------------------------------
1994년 성수대교 이후, 95년도에 재난관리법이
생기고, 2004년에 재난 및 안전관리기본법 제정.
2009년도 행정안전부에서 총괄 이후 2014년 안전행정부로 변경되면서 국민안전처까지 변경
현재는 미국이학회에서 만든 국가재난의료과정
(national disaster life support, NDLS)개발
기본재난대응과정(BDLS)
전문재난대응과정(ADLS)
핵심재난대응과정(CDLS)
재난의 전과정 PRE-DISASTER 등,
- P(계획과 연습) planning and practice
- R(재난에 대한 복원력) resilience
- E(교육과 훈련) education and training
- D(재난발생의 인지) detection
- I(지휘통제) incindent command
- S(현장안전) safety and security
- A(위험평가) assess hazard
- S(지원) support
- T(중증도 분류와 치료) triage and treatment
- E(대피) evacuation
- R(복구) recovery
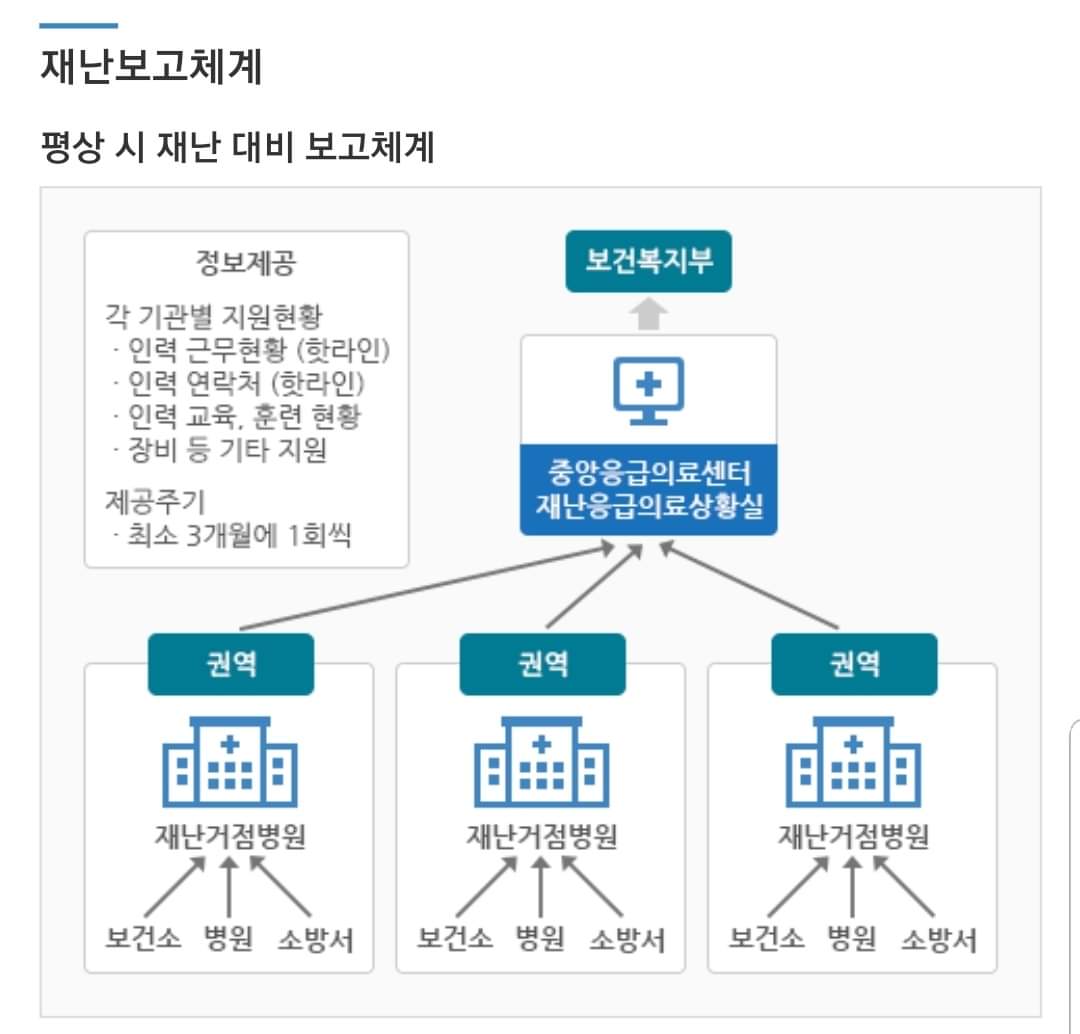
교육을 진행되고 있고, 중앙응급의료센터를 중심으로한 소방과 보건복지부를 비롯한 40개의 권역센터에서 현장에 DMAT을 파견하여, 재난의료체계를 구축하는 큰 그림으로 현재 보건복지부에서 발간한 '재난응급의료 비상대응매뉴얼'도 보급되었다.
또한 대량인명손상(MCI, multiple casualty incidents)에서기존의 중증도 분류법 이외에도
ㅇ START(simple triage and rapid transport)
ㅇ SAVE(secondary assessment of victim
end-point),
ㅇ SALT(sort, assess, lifesaving interventions, treat/transport) 등 여러가지 방법으로 연구 및 교육되고 있다.
ㅇ KTAS(Korean Triage and Acuity Scale)
ㅇ CTAS(Canadian Triage and Acuity Scale)
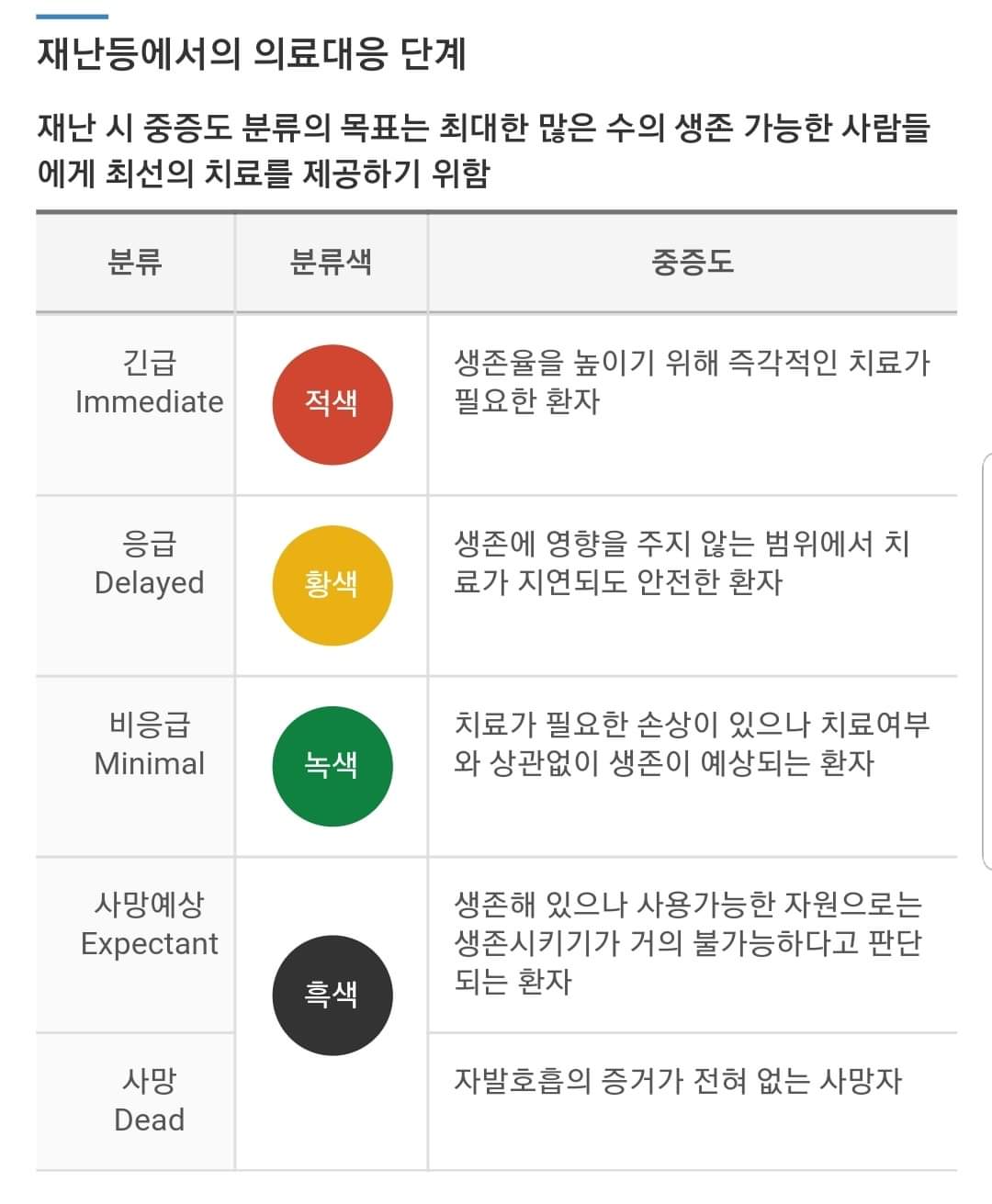
> 긴급(Immediate) 적색
- 생존율을 높이기 위해 즉각적인 치료가 필요한 환자
> 응급(Delayed) 황색
- 생존에 영향을 주지 않는 범위에서 치료가 지연되도 안전한 환자
> 비응급(Minimal) 녹색
- 치료가 필요한 손상이 있으나 치료여부와 상관없이 생존이 예상되는 환자
> 사망예상(Expetant) 흑색
- 생존해 있으나 사용가능한 자원으로는 생존시키기가 거의 불가능하다고 판단되는 환자
> 사망(Dead) 흑색
- 자발호흡의 증거가 전혀 없는 환자
Disaster emergency medical care! There are so many large and small disasters.
As a result, the contents of disaster medical care, which did not change in mass disaster data 20 years ago, seem to have gradually developed.
---------------------------------------------------------------
After Seongsu Bridge in 1994, the Disaster Management Act in 1995
It occurred, and in 2004, the Framework Act on Disaster and Safety Management was enacted.
After general supervision by the Ministry of Public Administration and Security in 2009, it was changed to the Ministry of Security and Public Administration in 2014, and the Ministry of Public Safety and Security was changed.
Currently, the National Disaster Medical Course created by the American Society of Science
(National disaster life support, NDLS) development
Basic Disaster Response Process (BDLS)
Professional Disaster Response Course (ADLS)
Core Disaster Response Process (CDLS)
Pre-DISASTER, etc.,
- P (Planning and Practice) Planning and Practice
- R (resilience to disasters) resilience
- Education and training (E)
- D (Cognition of disaster) detection
- I (command control) incindent command
- S (field safety) safety and security
- A (risk assessment) assessment hazard
- S (Support) support
- T (severe classification and treatment) triage and treatment
- E (evacuation) evacuation
- R (Recovery) recovery
Education is being conducted, and 40 regional centers, including the Ministry of Fire and Welfare, centered on the Central Emergency Medical Center, dispatched DMAT to the site to establish a disaster medical system, and the Emergency Response Manual for Disaster Emergency Medical Service currently published by the Ministry of Health and Welfare has also been distributed.
In addition to the existing severity classification method in multiple casualty incidents (MCI),
ᄋ Simple triage and rapid transport (START)
ᄋ Secondary assessment of victim (SAVE)
end-point),
ᄋ It is being researched and educated in various ways such as SALT (sort, assessment, lifesaving interventions, treat/transport).
ᄋ KTAS (Korean Triage and Acuity Scale)
ᄋ CTAS (Canadian Triage and Acuity Scale)
> Emergency red
- Patients who need immediate treatment to increase survival rate
> Delayed yellow
- Patients who are safe even if treatment is delayed to the extent that it does not affect survival
> Minimal green
- Patients who have damage that requires treatment but are expected to survive regardless of whether they are treated or not.
> Expetant black
- Patients who are alive but are judged to be almost impossible to survive with available resources.
> Dead black
- Patients with no evidence of spontaneous breathing
----------------------------------------------------------------------
2005년, 일본 재난의학에서 만든 재난의료지원단
DMAT(disaster medical assistance team)
1993년, 영국 ALSG (Advanced Life support group)에서 개발한 major incident, medical mangagement and support(MIMMS)과정을 교육하는 DMAT 과정등.
유럽연합 재난훈련 교과과정(disaster training curriculum, DITAC) 등27개국, 약 140개의 재난의학 교육 훈련과정 등이 있는데 우리나라는 미국과 일본의 DMAT 방식을 참고하고 있단다.
미국은 1985년부터 FEMA(Federal Emergency Management Agency)의 실행 조직으로 구성되고 27년간 약 50번 출동경험을 가지며 발전되었고, 일본의 경우 1995년도 한신 아와지 대지진 사건 이후 500명이 넘는 사망자를 통해 전문적인 재난의료지원 훈련을 받은 의료진과 행전요원들 구성의 필요성을 느끼고 2004년 8월에 창설되어 2010년까지 801개 팀(4,986명)이나 된다.
대만도 1999년 Chi-Chi 지역 지진으로 2000년 7월에 창설 후 9년간 약 2,500명 30개팀이 생겼다.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
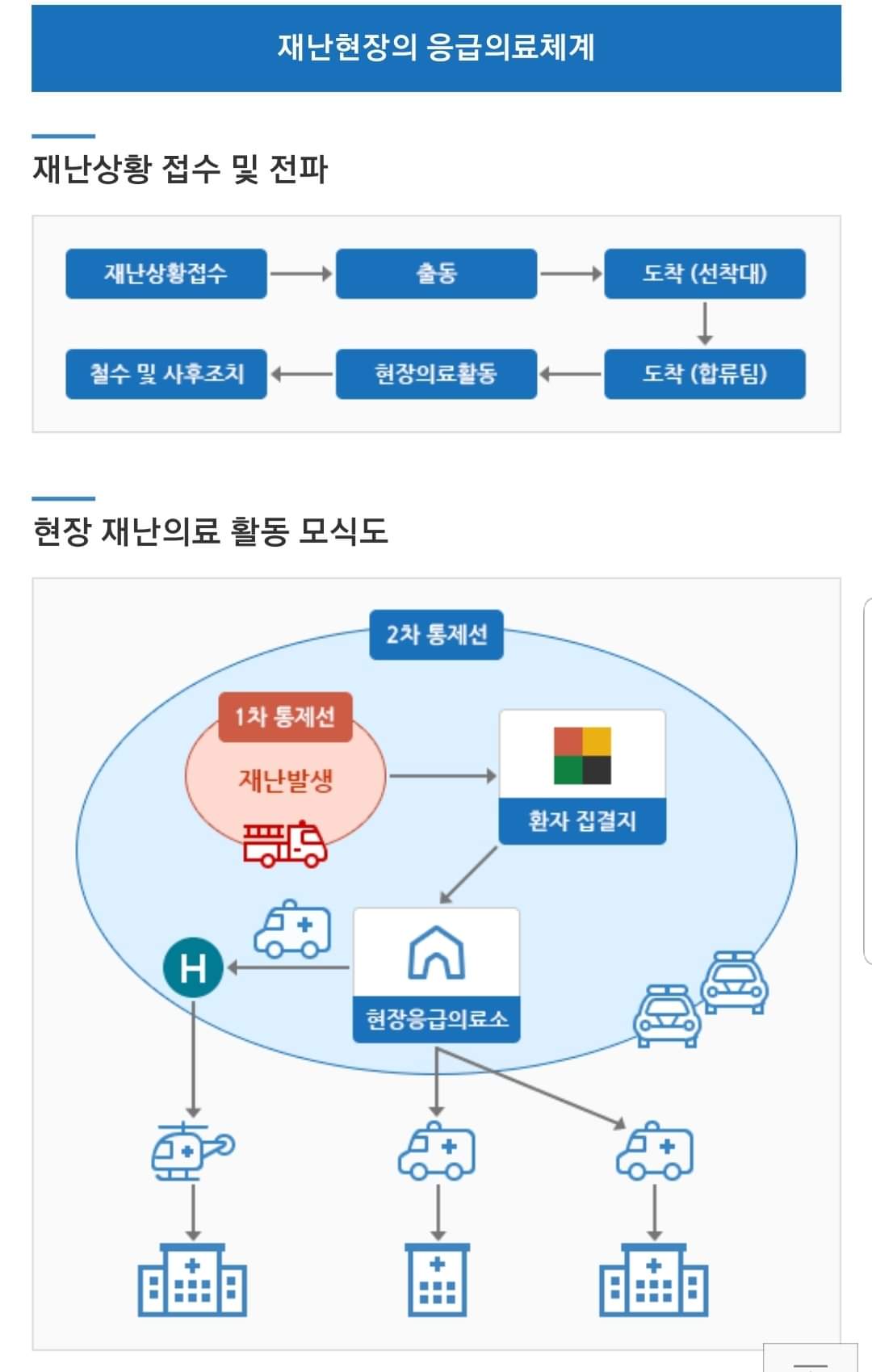
DMAT의 주요역할은 재난현장에서의 중증도 분류, 응급처치 및 이송이 주임무이다.
팀 당 의사 1명, 간호사/응급구조사 2명, 행정 1명 등 4명으로 구성된다.
보수교육 때 DMAT의 필요성에 대해 설명했는데
1. 소방의 초기 중증도 분류 및 분산이송 미실시.
2. 응급구조사의 현장응급처치의 한계
ex) Needle thoracostomy, Cricothyroidotomy, Amputation 등.
3. 법에는 현장에 의사 3명, 최소 1명 이상
현장응급의료소에 있어야 함.
ㅇ 재난발생시 응급의료체계 운용상 문제
1) 중증도 분류에 대한 인식부족 및 광역재난
현장에서 실질적인 적용의 어려움
2) 재난관제센터의 이송 병원의 수용능력 미고려
(중증도 합리적 환자 분산 실패)
3) 통제가 어려운 구급차 이외의 개별 이동 수단
으로 병원 방문
4) 현장 응급의료소 위치 홍보 부적절
5) 응급의료체계 통제 안받는 외부 구조자 참여
(큰 규모 혹은 도심 재난시 문제 발생)
6) 수색 구조팀과 응급의료체계간 협조관계 유지
실패
7) 조직간 유기적 대응계획의 미비 및 전체적 재난
상황에 대한 고려 / 평가 부족
8)상황분석과 환자 분산에 필수적인 현장 병원 간 통신부족
9) 전반적 상황통제가 가능한 직책을 가진 현장
지휘자 부족
In 2005, the Disaster Medical Support Group was created by Japan Disaster Medicine.
DMAT(disaster medical assistance team)
Major incident developed by Advanced Life Support Group (ALSG) in the UK in 1993, DMAT course to educate medical mangagement and support (MIMMS) course, etc.
There are about 140 disaster medicine education and training courses in 27 countries, including the European Union Disaster Training Curriculum (DITAC), and Korea refers to the DMAT method of the United States and Japan.
The United States has been composed of the FEMA (Federal Emergency Management Agency) implementation organization since 1985 and has developed with about 50 dispatch experiences over 27 years, and in Japan, after the 1995 Hanshin Awaji earthquake, more than 500 deaths caused the need to form medical staff and action personnel who received professional disaster medical support training, and it was established in August 2004 and had 801 teams (4,986 people) by 2010.
Taiwan also had about 2,500 people and 30 teams in the nine years since its establishment in July 2000 due to the 1999 Chi-Chi regional earthquake.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
DMAT's main role is to classify severity, first aid, and transfer at disaster sites.
It consists of four people per team: one doctor, two nurses/emergency investigators, and one administrator.
I explained the need for DMAT during refresher training.
1. Classification of initial severity of fire fighting and non-transfer of distribution.
2. Limitations of on-site emergency treatment by emergency responders
ex) Needle thoracostomy, Cricothyroidotomy, Amputation, etc.
3. The law states that there are three doctors and at least one doctor in the field.
You have to be in the field emergency medical center.
ᄋ Problems in the operation of emergency medical system in case of disaster
1) Lack of awareness of severity classification and wide-area disasters
Difficulties in practical application in the field
2) Non-consideration of the capacity of the transfer hospital of the disaster control center
(Severely reasonable patient dispersion failure)
3) Individual means of transportation other than ambulances that are difficult to control
Visit the hospital.
4) Inadequate promotion of the location of on-site emergency medical center
5) Participation of external rescuers who are not controlled by the emergency medical system
(Problems occur in large-scale or urban disasters)
6) Maintaining cooperative relationship between search and rescue team and emergency medical system
Failure
7) Inadequate organic response plans between organizations and overall disasters
Lack of consideration/evaluation of the situation
8) Insufficient communication between field hospitals essential for situational analysis and patient dispersion
9) Field with positions that can control the overall situation
Conductor tribe
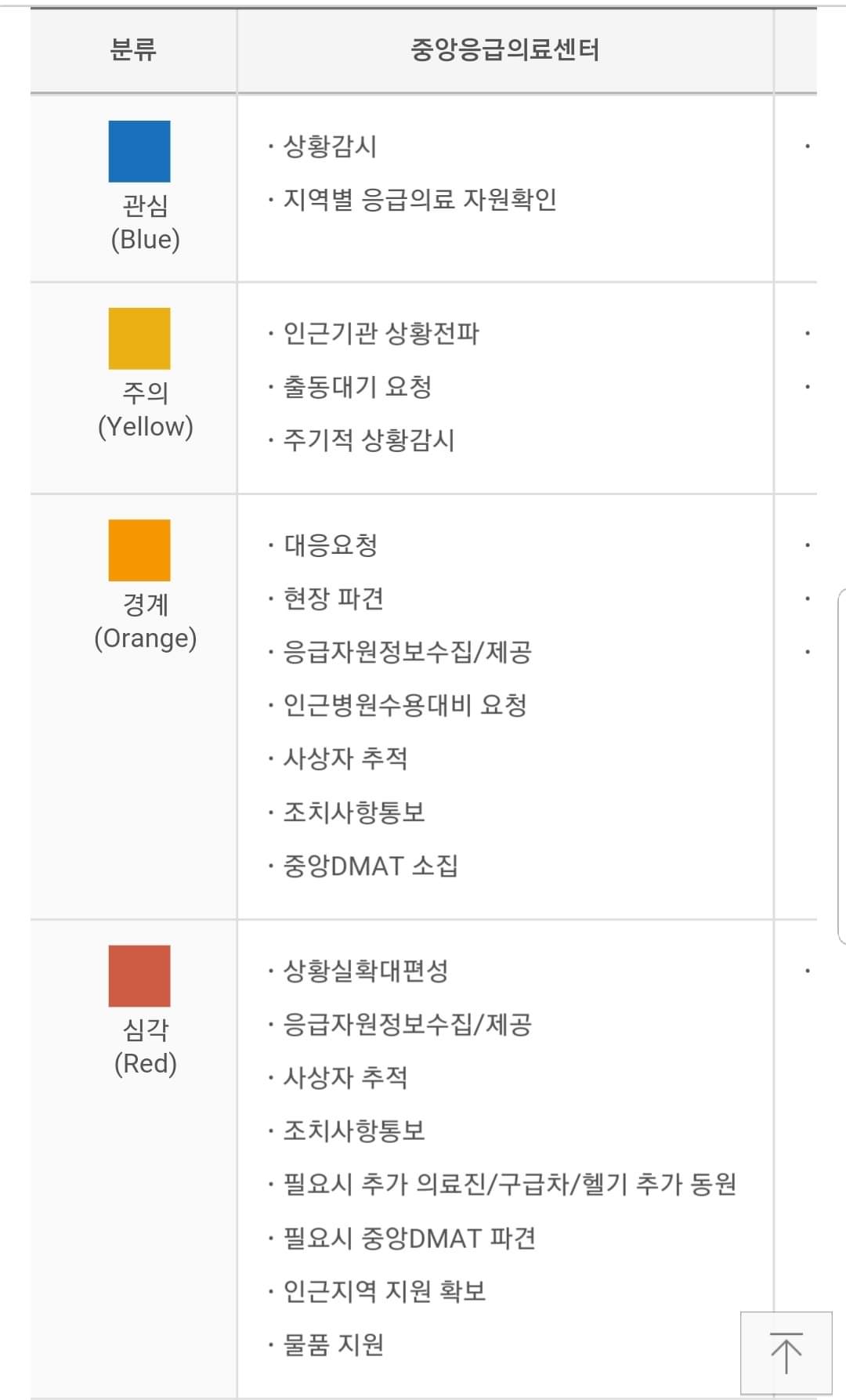
----------------------------------------------------------------------
ㅁ 개인적으로 예상되는 에로사항들...
1. DMAT이 현장이 오기전까지 현장에 초기대응팀으로 배정되어 있는 행정요원들은 보건소 직원들인데 인력도 많지 않지만, 24시간 대기가 아니기에 퇴근 후에는 어떻게 초기대응이 될지... 또한 보건소장이 현장대응 총괄관리할 만큼의 역량은 검증이 된 것인지
2. 핫라인으로 구성된 중앙, 재난응급의료상황실과 재난예방,상황요원들의 주된 Network 방식이 카톡방인 점도 App은 개발되고 있다하나, 재난의 종류에서 전시상황으로 된 후 통신망이 단절된다면?
이에 대한 가정은 준비된 것인지...
3. 무엇보다 사고가 발생된 후 DMAT이 소방보다 빨리올리가 없다는 것은 교육 때도 언급되었는데...
소방에서는 분류없이 단순히 이송만한다 가정한 것인지... 분명, 소방에서도 대량재해와 관련된 Triage kit 를 보유하고 있고, 훈련하는 것으로 알고있는데...
4. MCI 상황에서 현 우리나라 매뉴얼에서는 Simple Triage 분류법(START) 권장, 영구방식의 차이점은 있으나 해당 방식은 62~70%, SALT방식은 79~83%의 정확도를 보이는데 전자를 권장하는 이유는?
5. 지방 자치 단체 및 권역응급의료센터에서도 해마다 응급의료기관 평가를 통해 재난 관련 교육 상황을 평가받기 위해 자체 재난훈련받지만, 소방,경찰, 군인 등 각 부처들이 협력없이 따로 이루어지는 경우가 많은데 실제 통합된 지휘체계로 효율적으로 운영이 가능한지...
화재외에도 각종 안전사고, 건물 붕괴, 특히 화학물질 누출사고 등에도 전문적으로 통합대응을 할 수 있을지... 그것들을 가정한 시, 군부대, 응급의료센터, 소방 등 통합방재훈련을 여러차례 실시해본 결과, 현장대응 경험상 구조 및 제독, 제염, 응급처치, 현장분류소 등 모양세는 갖춰진 듯하나 DMAT의 현장활동 범위는 이론에 비해 한정적이었고, 중앙 지휘에서는 행정관료나 정치인에게 보여주기식 느낌이 강했다.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
ㅁ 개인적으로 생각한 대안의 일면들...
전쟁터에서는 지휘관이 누구냐에 따라 병사들의 생명이 오고간다. 재난 사고 현장에서도 마찬가지일 것이다. 총괄하는 지휘관이 누구냐에 따라 대응의 판도가 결정될 것이다. 그러기 위해서는 통합된 하나의 지휘체계에서 나머지 유관 기관들이 움직여야 할 것이다.
긴급구조대응 활동 및 현장지휘를 위해, 현장 안전을 확보, 통신체계 구성, 현장응급의료소를 설치하고, 현장 의료수요파악 및 후발대 요청, 중증도 분류, 응급처치, 이송 등의 기본적인 대응절차와 함께 현장대응은 100% 소방에서 맡게 될 것이고, 현장을 가장 잘아는 전문가들, 위험물이 있을 경우 특히 더 필요하며 현장의 지형과 Lay-out을 잘 아는 전문인력이 옆에서 도와야 할 것이다.
구조와 함께 다수환자에서, 최초의 현장 중증도 분류도 소방의 응급구조사가 주도해야 한다.
DMAT의 주업무가 TTT, 환자분류(triage), 응급처치(treatment), 이송(transportation)에 있다면, 환자분류는 현장응급의료서에서 해당한다.
교육 때, 문제삼은 응급구조사의 처치한계 따윈 핑계가 되지 않는다. 현장에서 단순 분류작업이 더 많은 사람을 살린다고 가르치고 배우지 않았는가?
얘기한 Needle thoracostomy, Cricothyroidotomy는 해당 현장에서 몇이나 발생하겠는가? 출동하는 DMAT이나 중앙응급의료센터에서 의료지도를 하던가 응급구조사의 업무범위를 재난시에라도 허가하면 되지 않는가?
(의료범위확대 문제는 책임소지 등으로 더이상 거론하지 않기로 함)
Amputation은 사유 자체도 되지 않는다.
기본적으로 응급구조사의 Skill 을 신뢰하지 않는 가정하에 짜여진 듯한 느낌이다)
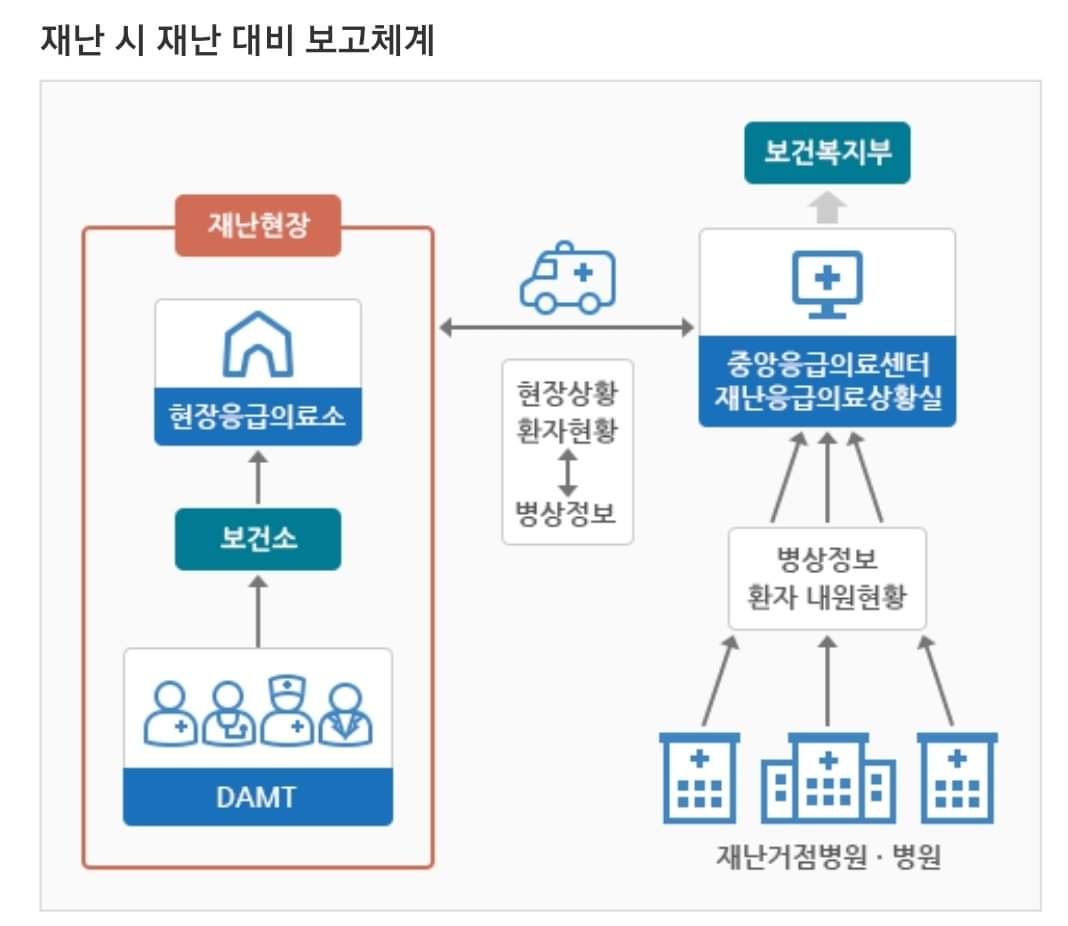
반면에 지휘체계의 혼란을 막기위해, 일단 보건소장을 현장응급의료소 운영총괄로 맡은 것은 좋다. 오히려 정해놓지않고 애매한 것이 더 혼란을 가중시키기 때문이다. 또한 중앙응급의료센터에서 재난응급상황시 현장상황을 파악하고 병상정보 등을 미리 알려줘서 2,3차병원으로 분산 이송될 수 있도록 구분한 것도 좋다.
다만, 단순 사고로 인한 한채널의 사고도 환자에 대한 잘못된 정보나 잘못된 장소 등 정보 교환에서 에러사항이 발생할 수 있기 때문에, 유관부서들과의 유기적인 Co-work을 위해 매뉴얼 숙지와 훈련은 필수 적일 것이다.
또한 실질적으로 소방과 병원의 구급차로 이송이 어려운 부분들을 민간이송업의 구급차가 많이 이용될텐데..이 부분에서 분류된 병원으로의 이송을 위한 정보 지시도 구체적이고 명확한 채널을 마련해야할 것 같다.
Gas, Chemical 등의 사고에 대한 부분은 현장대응팀이 고생하지 않도록 누출 물질에 대한 정확한 정보제공과 함께 ALOHA program 같은 프로그램 활성화를 통해 사고피해 예측결과를 확인하고, Simulation이 구글 어스와 연결되어, 피해정도에 대해 Map 으로 표시되며, 풍향까지 계산되어 나오니 활용하면 좋지 않을까 싶다.
Toxic 노출시, 해발고도, 위도, 경도, 건물환기횟수
물질명, 풍속, 풍향(최대 북동편), 온도, 습도 등.
ᄆ Personal expected eros...
1. Administrative personnel assigned to the site as initial response teams until DMAT comes to the site are health center employees, but there are not many personnel, but they are not waiting 24 hours a day, so how to respond in the early stages after work... In addition, whether the capacity of the head of the public health center to manage on-site response has been verified.
2. The fact that the main network method of the central, disaster emergency medical situation room, disaster prevention, and situation personnel composed of hotlines is KakaoTalk is also being developed, but what if the communication network is cut off after the type of disaster becomes an exhibition situation?
I don't know if the assumption about this is ready...
3. Above all, it was also mentioned in the training that DMAT does not raise faster than fire after an accident...
Is it assumed that the fire department simply transfers without classification... Obviously, fire fighting also has a carriage kit related to mass disasters, and I know it trains...
4. In the MCI situation, the current Korean manual recommends the Simple Triage Classification (START) and the permanent method, but the accuracy of the method is 62-70% and the SALT method is 79-83%, so why is the former recommended?
5. Local governments and regional emergency medical centers also receive their own disaster training every year to evaluate disaster-related educational conditions through the evaluation of emergency medical institutions, but each ministry, including fire, police, and soldiers, is often carried out separately without cooperation, so is it possible to operate efficiently with an actual integrated command system?
In addition to fire, whether it will be able to respond professionally to various safety accidents, building collapse, especially chemical leakage accidents... As a result of conducting integrated disaster prevention drills such as cities, military units, emergency medical centers, and fire fighting, assuming them, the field response experience seemed to have a structure, admiralty, decontamination, first aid, and field classification centers, but the scope of DMAT's field activities was limited compared to the theory, and the central command had a strong sense of showing to administrative officials and politicians.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
ᄆ One aspect of the alternative I personally thought...
On the battlefield, the lives of soldiers come and go depending on who the commander is. The same will be true at the scene of disaster accidents. Who is the commander in charge will determine the outcome of the response. To do so, the rest of the related organizations will have to move in one integrated command system.
For emergency rescue response activities and on-site command, on-site response will be 100% handled by fire fighting, along with basic response procedures such as securing on-site safety, forming a communication system, setting up on-site emergency medical centers, identifying on-site medical demand, requesting latecomers, classifying severity, first aid, and transfer, and experts who know the best of the site, especially if there are dangerous goods, will have to help from the side.
In many patients along with rescue, the first on-site severity classification should also be led by emergency medical technicians of firefighting.
If DMAT's main task is TTT, patient classification, treatment, and transport, patient classification corresponds to on-site emergency medical centers.
In education, the problem is not an excuse for emergency medical personnel to limit treatment. Didn't you teach and learn that simple sorting work saves more people in the field?
How many Needle thoracostomy and Cricothyroidotomy will occur at the site? Can't we provide medical guidance at the dispatched DMAT or the Central Emergency Medical Center or permit the scope of emergency medical personnel's work even in case of a disaster?
(We will no longer discuss the issue of expanding the scope of medical care due to responsibility.)
Amputation is not a reason itself.
Basically, it feels like it's woven under the assumption that you don't trust the emergency technician's Skill.)
On the other hand, in order to prevent confusion in the command system, it is good to take over the head of the public health center as the general manager of the operation of the on-site emergency medical center. Rather, it is because ambiguity without a decision adds to the confusion. In addition, it is good to classify the central emergency medical center so that it can be distributed to secondary and tertiary hospitals by identifying the on-site situation in case of a disaster emergency and informing them of bed information in advance.
However, since one channel accident due to a simple accident may also cause errors in information exchange such as wrong information about patients or wrong places, familiarity with manuals and training will be essential for organic co-work with related departments.
Also, ambulances in the private transportation industry will be used a lot for areas that are actually difficult to transport by ambulances in fire departments and hospitals. It seems that specific and clear channels should be provided for information instructions for transfer to hospitals classified in this part.
Accidents such as Gas and Chemical are confirmed by providing accurate information on leaked materials and activating programs such as ALOHA programs to prevent on-site response teams from suffering, and simulation is connected to Google Earth, displayed as a map on the degree of damage, and wind direction is calculated, so it would be good to use it.
When exposed to Toxic, altitude above sea level, latitude, longitude, number of building ventilation
Material name, wind speed, wind direction (maximum northeast), temperature, humidity, etc.







----------------------------------------------------------------------
* 개인적인 문제 제기와 대안들은 전문가가 아니라서 실제 구축된 시스템의 디테일과 다를 수 있으며, 교육에서 든 느낌에 대한 서술이니 참고바랍니다.
전쟁나면, 최대한 움직이지 말고 화생방피해를 막기위해 창문을 닫고 테이핑처리하고 기본적인 식수를 확보하고 지하주차장이나 대피소로 피하시오!라는 등의 어의없는 재난 대응 매뉴얼이 탄생하고, 그안에 응급구조사가 일면을 담당하는 일이 없길 바란다.
#대량재해 #재난응급의료 #다수사상자
#DMAT #국가재난의료 #중증도분류 #재난의료
#응급구조사 #triage #SALT #재난 #Disaster
#START #중증도분류 #환자분류
ㅇ 참고자료
- 재난의학 교육 및 훈련/논문
- 재난응급의료 서비스/논문
(세브란스병원 재난대응 의료안전망 교육센터)
- 국가재난의료관리체계 설계 및 표준매뉴얼
- 재난의료지원팀/논문_원주의과대학 응급의학
- 재난응급의료 비상대응매뉴얼
- 대량재해 다수사상자 중증도 분류
- National Disaster Life Support Foundation
- Diaster Management. National Critical
Care and Trauma Response Center
- Major Incident medical management and
support(MIMMS)
- 중앙응급의료센터 재난대응체계
* Personal problem raising and alternatives may be different from the details of the actual system because they are not experts, and please refer to it as a description of the feelings of education.
In the event of a war, don't move as much as possible, close the windows, tap them, secure basic drinking water, and avoid underground parking lots or shelters to prevent CBR damage! I hope that an unintentional disaster response manual such as will be created, and emergency medical technicians will not take charge of one side in it.
# Mass disaster # disaster emergency medical care # multiple casualties
#DMAT #National Disaster Medical #Severe Classification #Disaster Medical
# Emergency Investigation #Triage #SALT #Disaster #Disaster
#START # Severe Classification # Patient Classification
ᄋ Reference
- Disaster medicine education and training/paper
- Disaster emergency medical service / thesis
(Severance Hospital Disaster Response Medical Safety Net Education Center)
- Design and standard manual of national disaster medical management system
- Disaster Medical Support Team / Paper_Emergency Medicine at Wonju Medical School
- Emergency Response Manual for Disaster Emergency Medical Care
- Classification of severity of mass disasters and multiple casualties
- National Disaster Life Support Foundation
- Diaster Management. National Critical
Care and Trauma Response Center
- Major Incident medical management and
support(MIMMS)
- Disaster response system of Central Emergency Medical Center







혹시나 하는 마음에 집에 하나 사뒀다!
K-RATION 생존배낭 A세트 40L (3일) 전쟁배낭 재난대비배낭 지진가방 전쟁가방
COUPANG
www.coupang.com
'일반의학 General Medicine' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 진단명 모음 (0) | 2020.11.15 |
|---|---|
| 응급구조사가 알아야하는 Anaphylaxis 아나필락시스 (0) | 2020.06.10 |
| 응급구조사가 알아야할 기초영어표현 I (0) | 2020.05.24 |
| 응급구조사가 알아야할 쇼크(Shock) (0) | 2020.05.15 |
| 응급구조사가 알아야할 호흡 Respiration, Breathing that emergency medical technicians need to (0) | 2020.05.14 |



